Command Line Utilities in Linux
LS: This command is used for listing contents inside a directory
It can be called by
lsdirectly or with flags like:ls -lDisplay All Information About Files/Directoriesls -tOpen Last Edited Filels -1One File in Each Linels -hDisplay File Size in Human Readable Format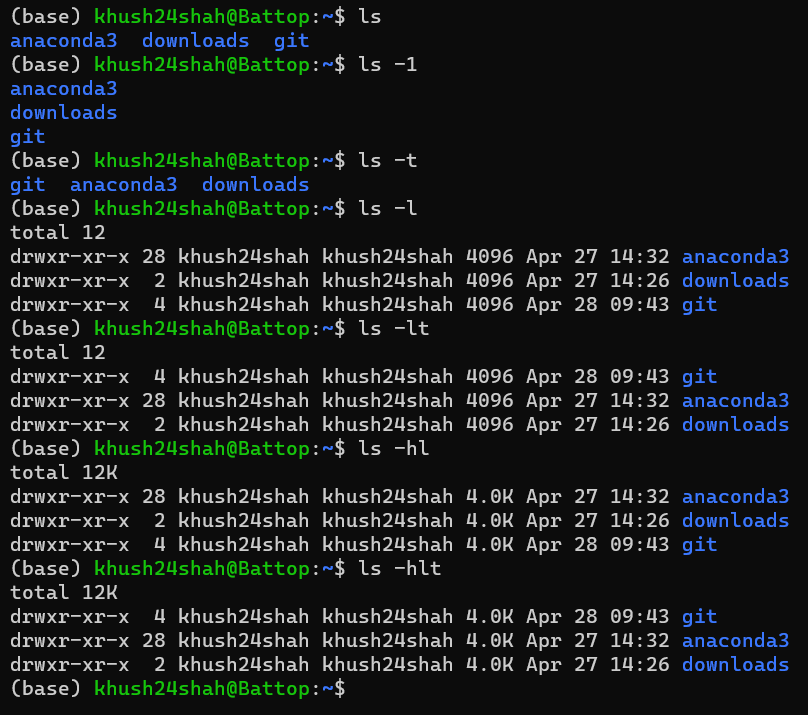
CAT: This command reads each file parameter in sequence and writes it to standard output.
It can be called by
cat <fileName>directly or with flags like:cat -nNumber All Output Linescat -bNumber Nonempty Output Linescat -sSuppress Repeated Empty Output Lines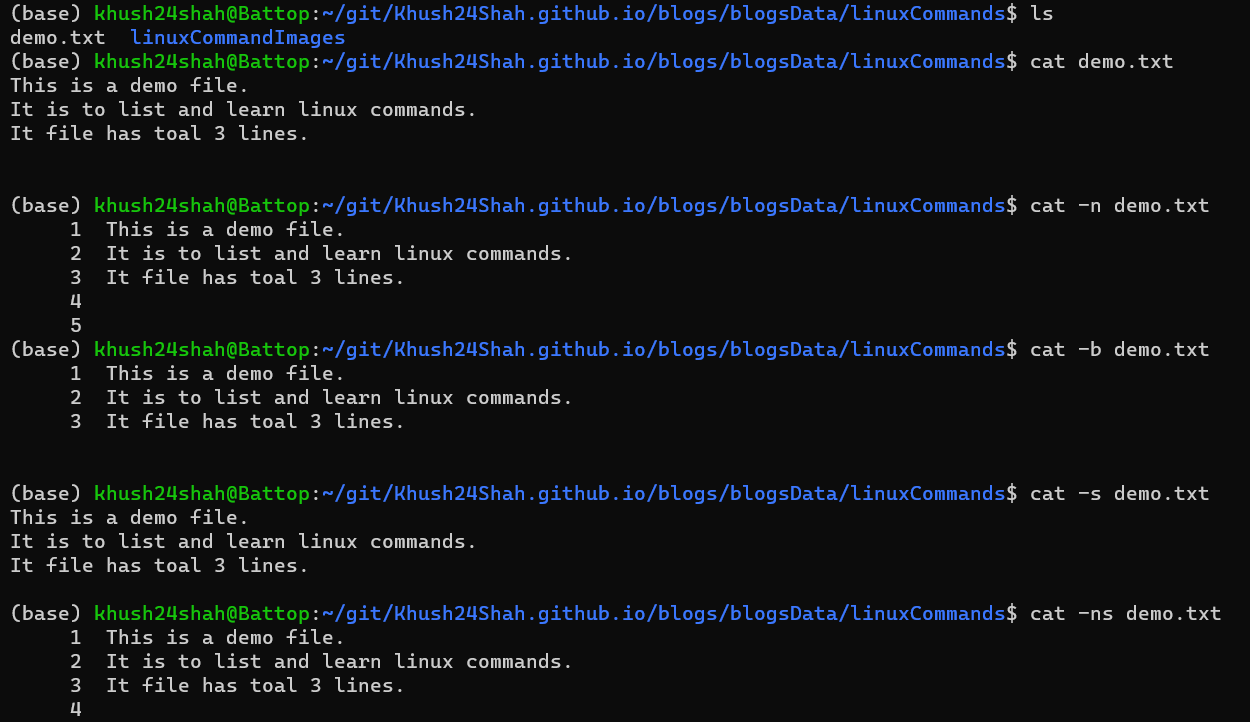
BAT:
batis acatclone with Syntax Highlighting and Git Integration.To Install Bat on Linux system (with Ubuntu), run command
sudo apt install bat.It can be called by
batcat(in Ubuntu). To check its version run commandbatcat --version.It can be called by
batcat <fileName>directly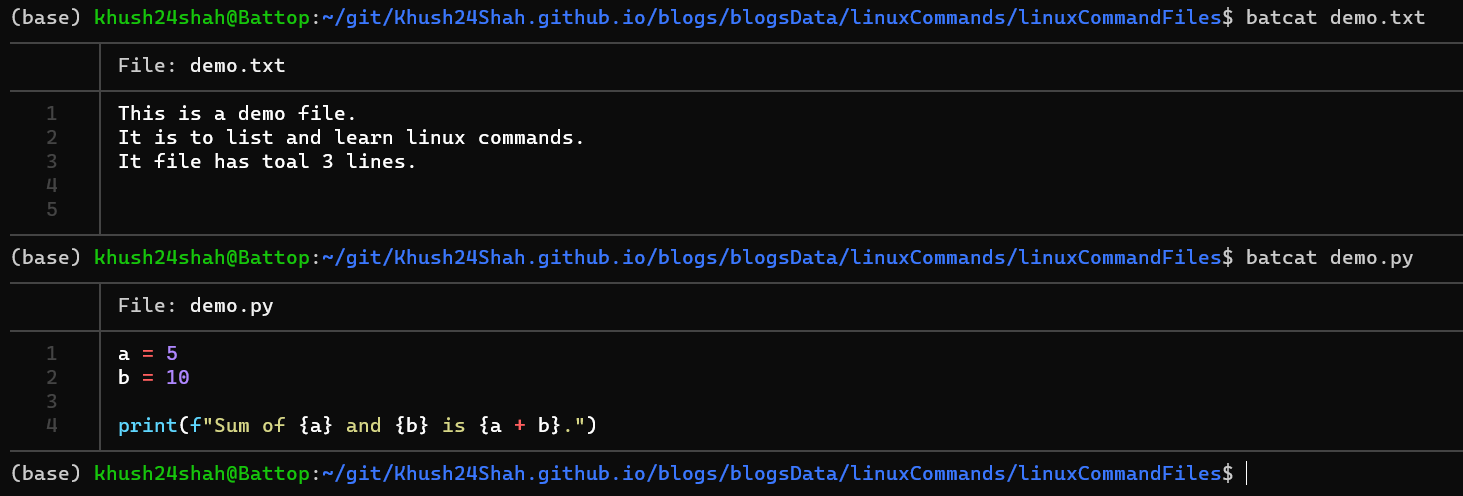
MKDIR: This command is used for creating a new directory.
It can be called by
mkdir <directoryName>directly or with flags like:mkdir -vPrint a message for each created directory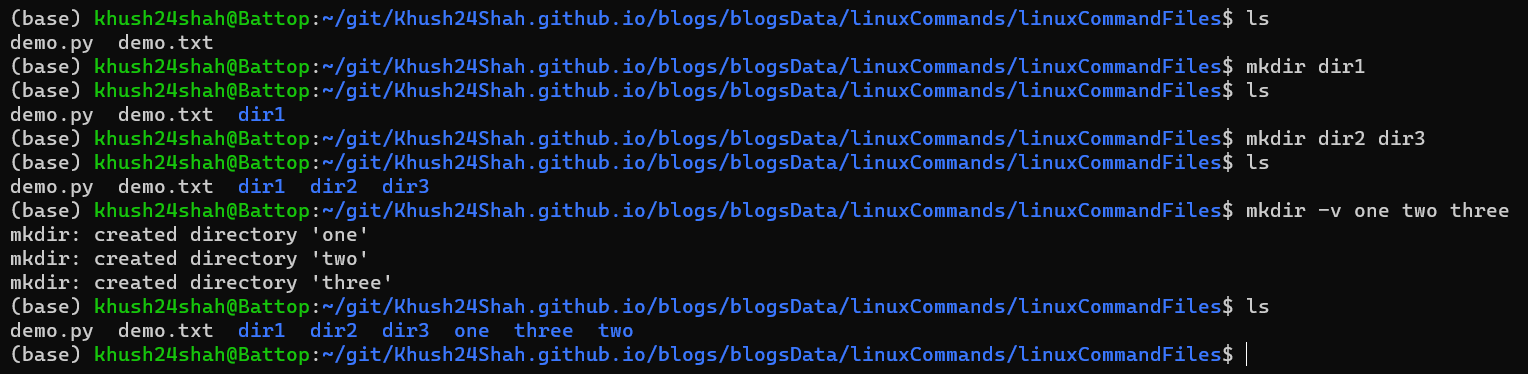
CD: This command is used for changing the current directory.
It can be called by
cd <directoryName>directly to change the directory to the specified directory.cd ..(..as an argument) can be used to change the directory to the parent directory.cd(without any argument) can be used to change the directory to the home directory.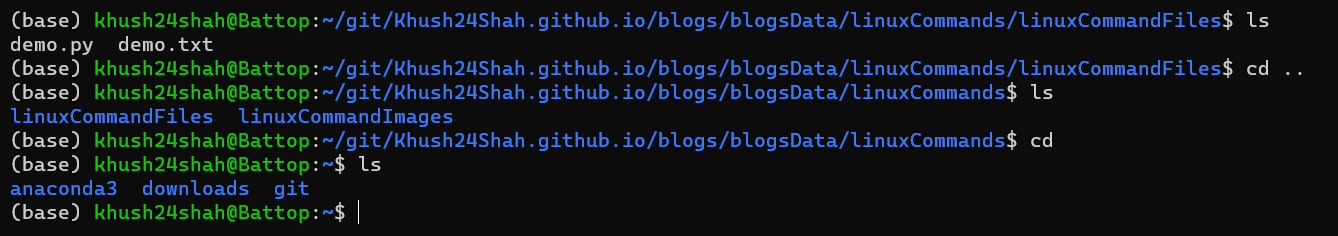
TOUCH: This command is used for creating a new file.
touch <fileName>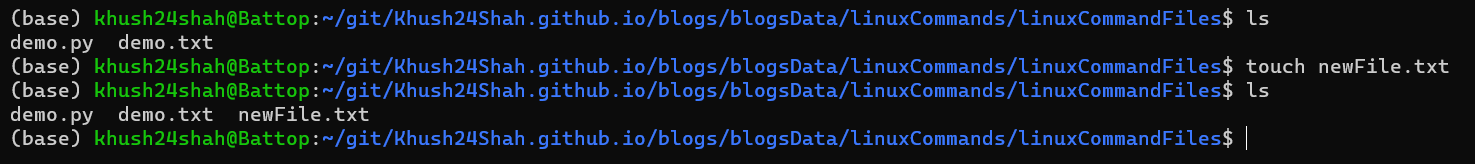
ECHO: This command is used for printing a line of text/string that are passed as an argument.
echo "This is ECHO command."It can also be used to write text to a file by using
>(Rewrite) or>>(Append) operator.echo "This is a new file." | cat > newFile.txtwrites the text “This is a new file.” to the newFile.txt file.echo "This rewrites the file." | cat > newFile.txtrewrites the newFile.txt file with the text “This rewrites the file.”echo "This appends a new line in the file." | cat >> newFile.txtappends the text “This appends a new line in the file.” to the newFile.txt file.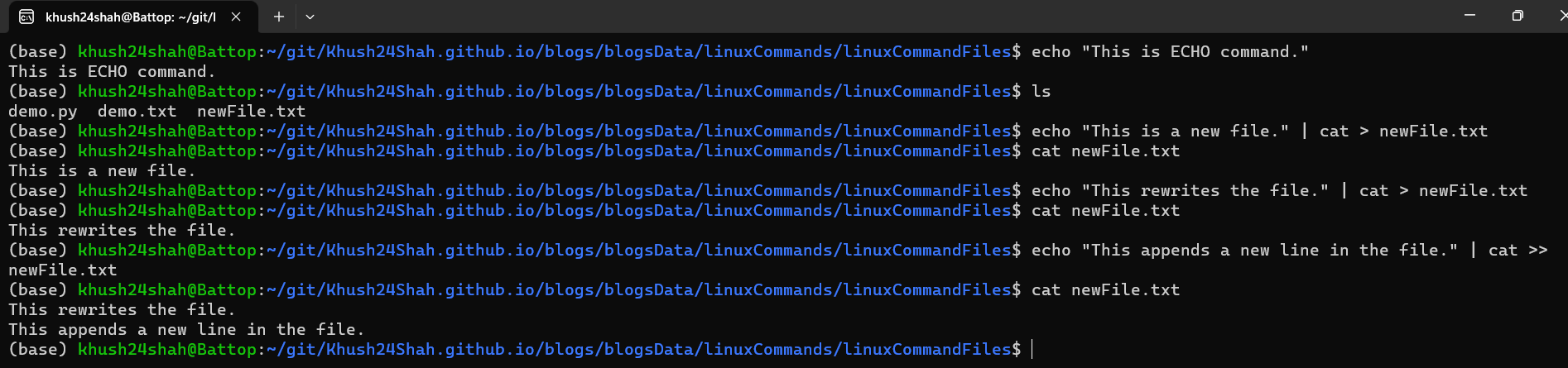
RM: This command is used for deleting a file or directory.
It can be called by
rm <fileName>directly or with flags like:rm -vPrint a Message for Each Removed Filerm -iPrompt Before Every Removalrm -fIgnore Nonexistent Files and Arguments and Remove Them Forcefullyrm -dRemove Empty Directoriesrm -rRemove Directories and Their Contents Recursivelyrm -rfRemove Directories and Their Contents Recursively and Forcefully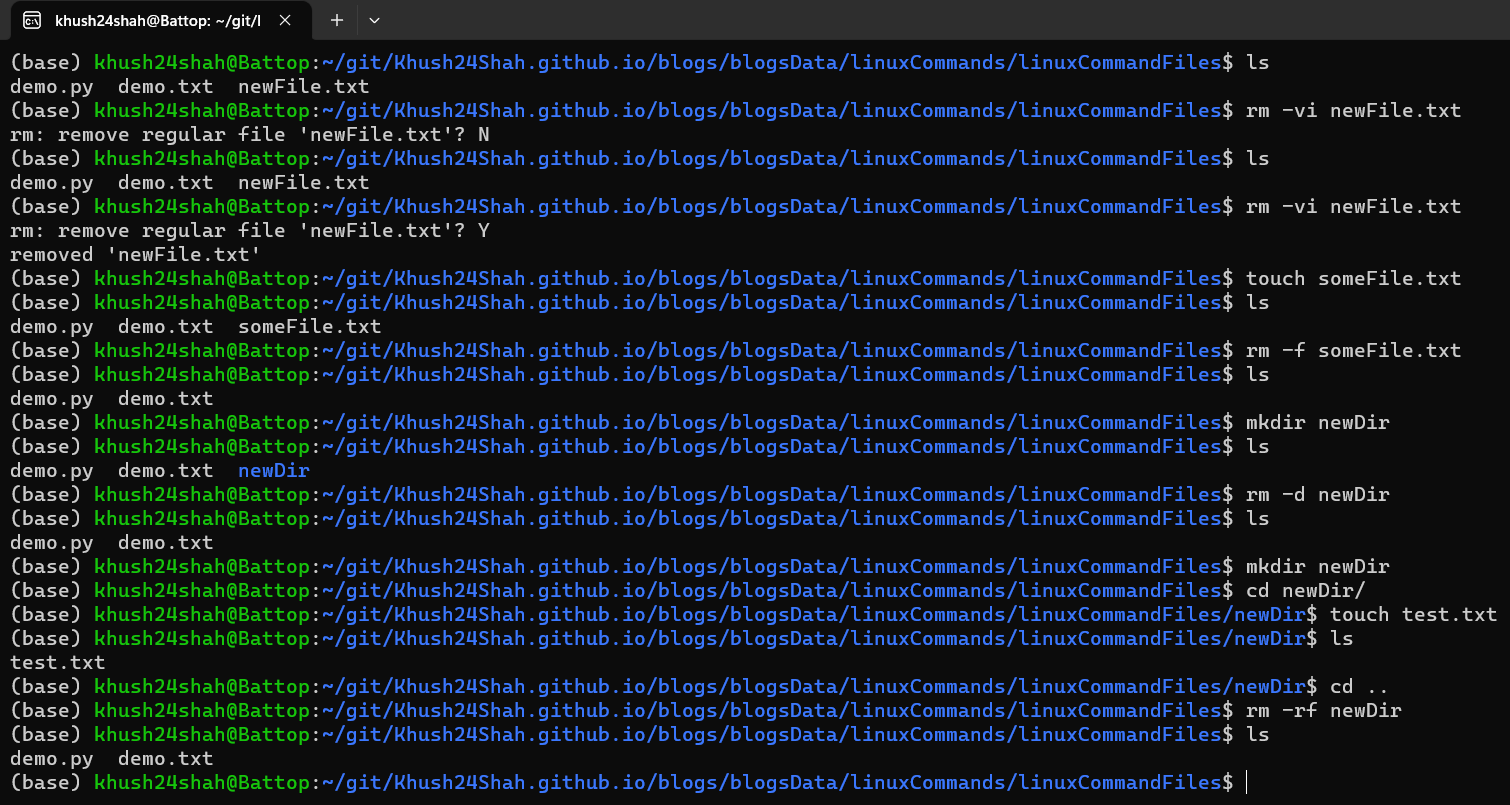
MV: This command is used for moving a file or directory to another location.
It can be called by
mv fileName destinationDirectorydirectly or with flags like:mv -vPrint a Message for Each Moved Filemv -iPrompt Before Overwritingmv -fIgnore Nonexistent Files and Arguments and Move Them Forcefullymv -nDo Not Overwrite an Existing Filemv -rMove Directories and Their Contents Recursivelymv fileName newFileNamerename a file/directory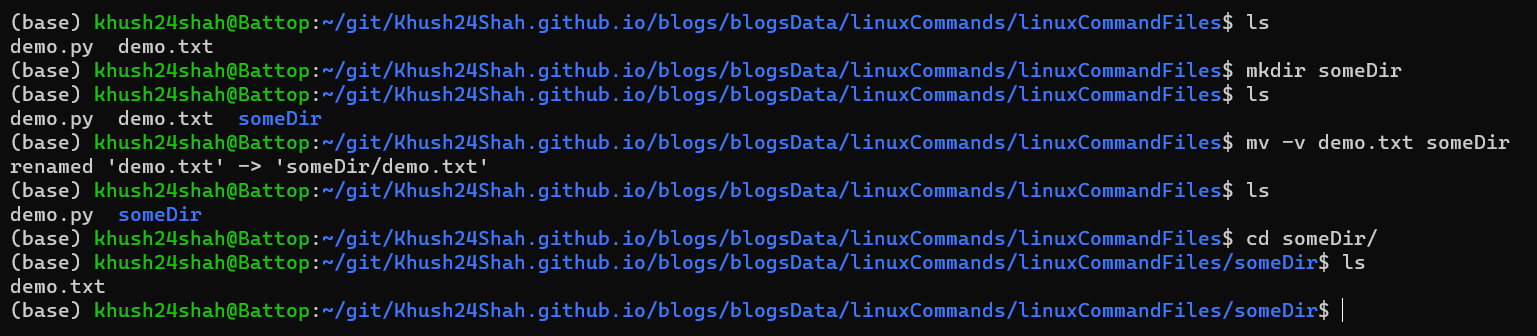
CP: This command is used for copying a file or directory to another location.
It can be called by
cp fileName destinationDirectorydirectly or with flags like:cp -vPrint a Message for Each Copied Filecp -iPrompt Before Overwritingcp -fIgnore Nonexistent Files and Arguments and Copy Them Forcefullycp -nDo Not Overwrite an Existing Filecp -rCopy Directories and Their Contents Recursively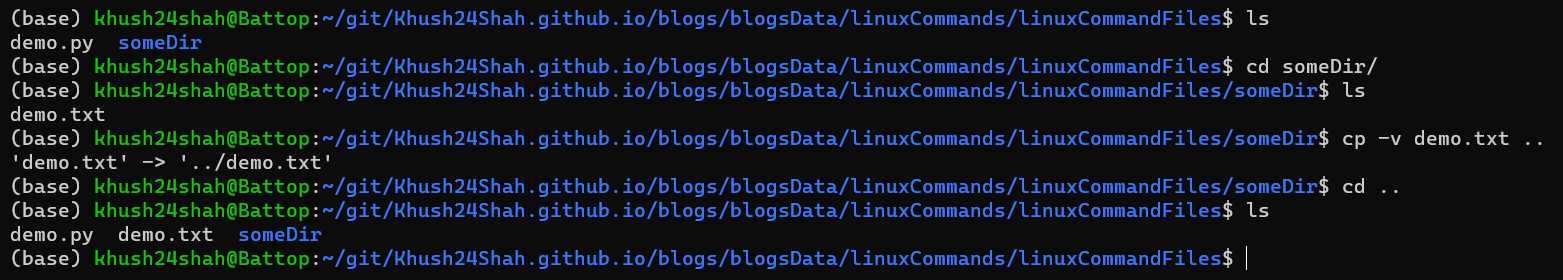
TREE: This command is used for displaying the directory structure in a tree format.
To Install Tree on Linux system (with Ubuntu), run command
sudo apt install tree.It can be called by
tree(in Ubuntu). To check its version run commandtree --version.It can be called by
treedirectly or with flags like:tree -aDisplay All Files and Directoriestree -dDisplay Directories Onlytree -L <level>Display Directory Structure to a Specified Leveltree -fDisplay Full Path for Each Filetree -iDo Not Print Indent Linestree -vSOrt Files and Directories Alphanumerically by Versiontree -tSort Files and Directories by Last Modified Timetree -hPrint the Size of Each File in a Human Readable Formattree -QQuote Each File Name with Double Quotes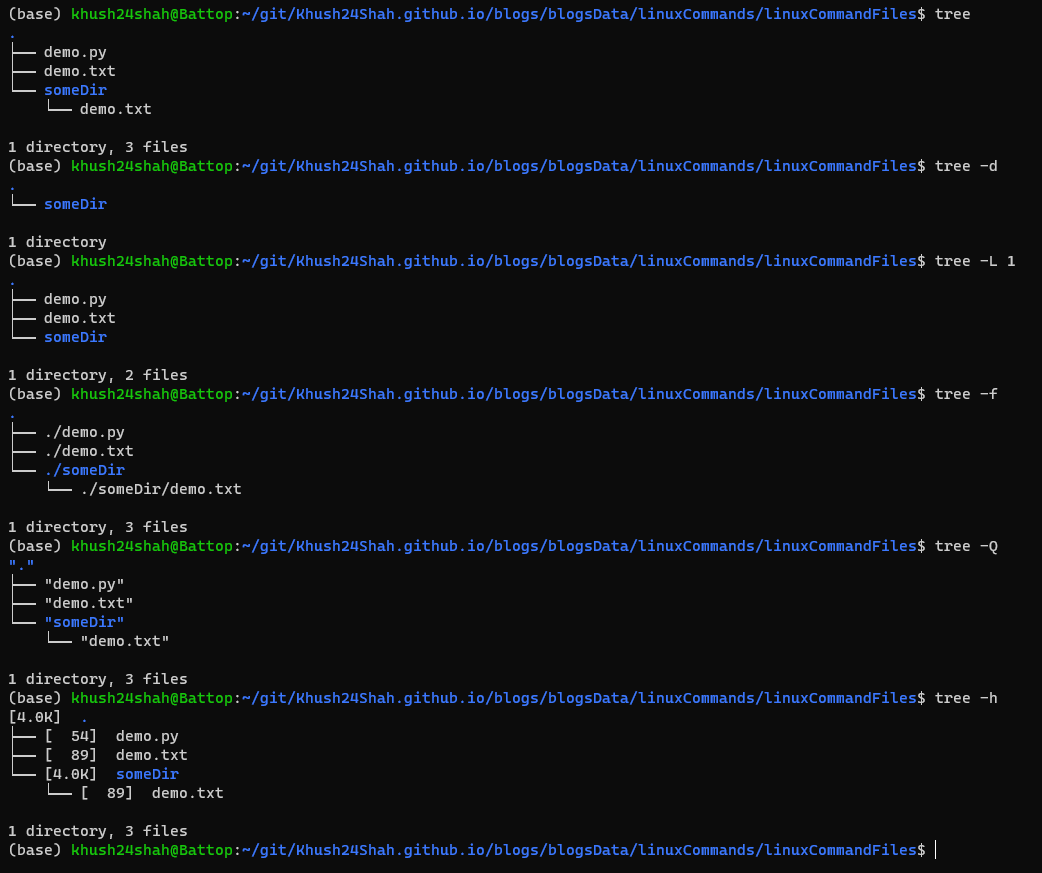
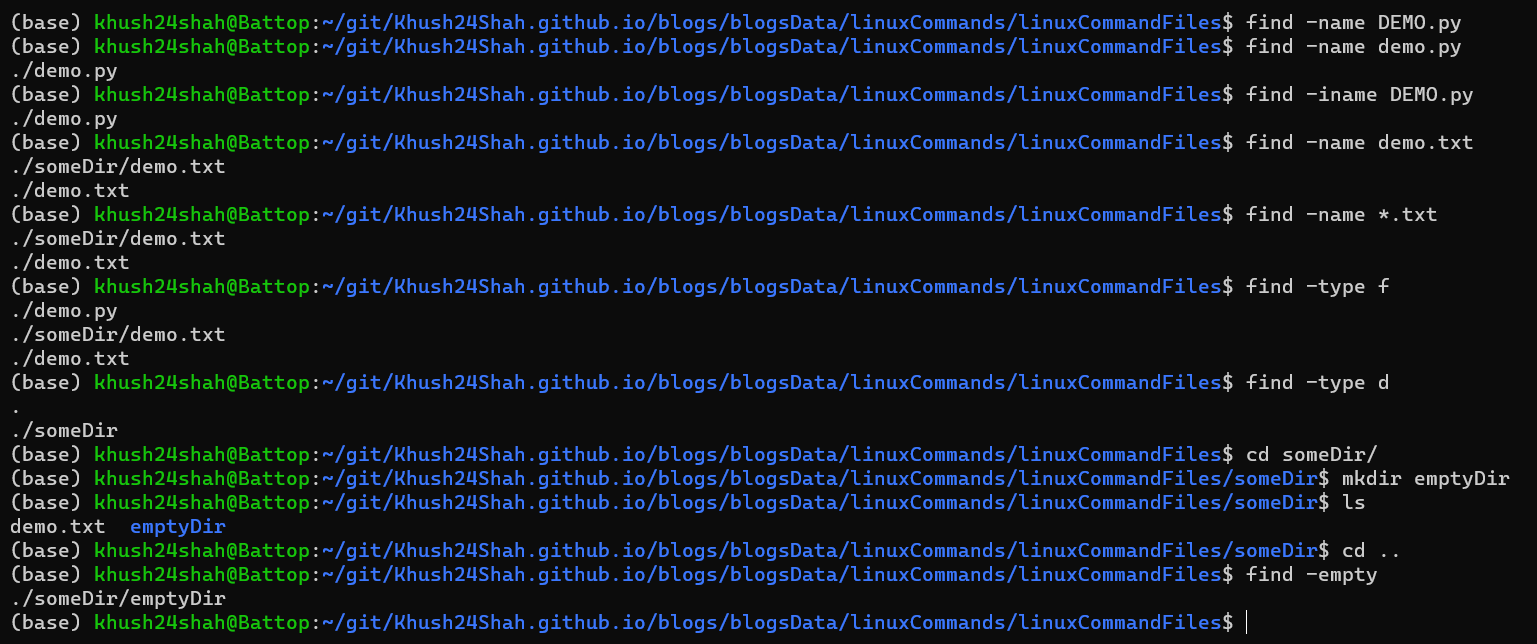
FIND: This command is used for finding files and directories in a directory hierarchy.
It can be called by
find <directoryName>directly or with flags like:find -name <fileName>Find a File by Namefind -iname <fileName>Find a File by Name (Case Insensitive)find -type <fileType>Find a File by Typefind -emptyFind an Empty File or Directory